The security industry has been using the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) since 2003 to help assess the severity of computer security vulnerabilities. This system has gone through several iterations as the criteria being reviewed have been updated to try and keep pace with the evolving threat landscape. These ratings are likely familiar to you, but you may have seen vulnerabilities being referenced in a few different ways. The first one worth noting is the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog. This doesn’t need much further discussion as the name says it all. This listing includes vulnerabilities CISA has seen being actively exploited and should already be included in your vulnerability management program. The second rating system you may have seen is the Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS), which is what we’re focusing on today.
What is the EPSS?
The Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS) 3.0 is a comprehensive, efficient, and effective model that provides a numerical score of how likely a vulnerability is to be exploited over the next 30-day period. The creation of this was driven by the following:
- Organizations can generally fix 5%-20% of vulnerabilities in any given month
- Only 2%-7% of published vulnerabilities are exploited in the wild
The EPSS aims to help organizations prioritize vulnerabilities that pose the most risk and those that are the most likely to be exploited. The EPSS model helps organizations minimize the burden of patching critical vulnerabilities with one-eighth of the effort of typical strategies using CVSS. EPSS utilizes a variety of sources when it comes to exploits and has a strong data-driven approach to evaluating threats.

Source: https://www.first.org/epss/model
How is EPSS calculated?
The EPSS collects data from several sources, but it is worth noting that it does include CVSS v3 Base Scores, meaning you can leverage existing processes built around CVSS and use the EPSS to augment your remediation efforts. The EPSS also considers sources such as the existence of exploit code and the age of the vulnerability. In total there are over 1,000 variables that are considered, and the full details are available on the FIRST page.
Why does this matter?
Many organizations build their vulnerability management program around the CVSS score, and many compliance efforts use these same CVSS scores for ratings (e.g., PCI DSS). While this is well intentioned, the CVSS places weight on the potential impact should the vulnerability be exploited, without consideration of the likelihood that this will be exploited. At best, this leads to an inefficient vulnerability management process, and at worst it leaves you vulnerable to actively exploited vulnerabilities while you chase down theoretical risks. The ideal approach would be to evaluate both the CVSS and the EPSS scores to determine which vulnerabilities will be addressed first. Those scoring high on both CVSS and EPSS are issues that are very likely to be exploited within the next 30 days, and are also likely to have a significant impact on your environment.
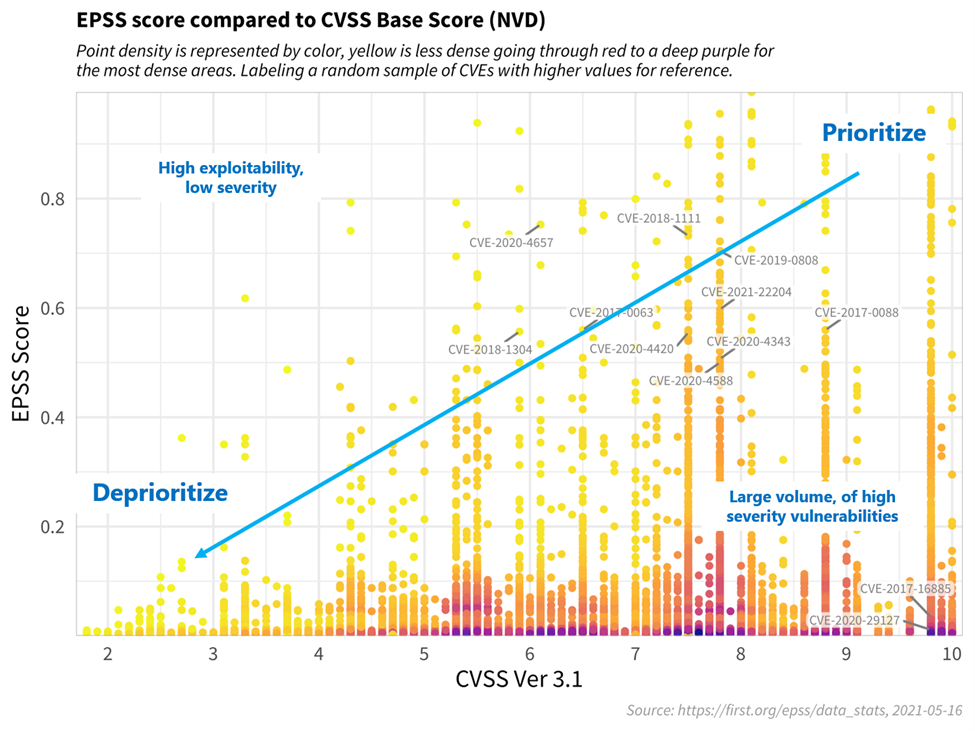
Source: https://www.first.org/epss/user-guide
In a world with limited resources, EPSS helps organizations make informed decisions about which vulnerabilities to prioritize for remediation based on their specific risk tolerance and resource constraints. Focus your defensive efforts where the attackers are most likely to be.
If you’re looking for an assessment of your current efforts, reach out to our experts at DenSecure today.